Now Reading: Top 10 In-Demand Skills for 2025
-
01
Top 10 In-Demand Skills for 2025
Top 10 In-Demand Skills for 2025


Last Updated: April 27, 2025
Are you prepared for the rapidly evolving job market? According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, approximately 170 million new jobs will be created between 2025 and 2030, with 92 million roles being displaced, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs globally. This significant workforce transformation means nearly 40% of workers’ core skills are expected to change by 2030.
Technical Skills

The technological transformation of workplaces continues to accelerate in 2025, making certain technical capabilities essential across virtually all industries. According to the World Economic Forum’s latest research, technology-related skills are expected to grow in importance more rapidly than any other type of skills in the next five years, with the skills gap being the most significant barrier to business transformation for 63% of employers surveyed.
The data is clear: if the world’s workforce comprised 100 people, 59 would need training by 2030, with 29 able to be upskilled in their current roles, 19 potentially redeployed within their organizations after upskilling, and 11 at risk without proper reskilling. These technological skills are no longer confined to IT departments but have become fundamental requirements for professionals at all levels and sectors.
1. AI Literacy

Artificial Intelligence has transcended its status as a specialized field to become an integrated component of everyday professional life. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 identifies AI and big data as the fastest-growing skills in the job market, with over 90% of respondents across most industry sectors expecting these skills to increase in importance by 2030.
What AI Literacy Entails in 2025:
- Understanding AI Capabilities: Knowledge of what modern AI systems can and cannot do, including generative AI tools and their limitations
- Critical Assessment: Ability to evaluate AI outputs, recognize limitations, and identify potential biases
- Advanced Prompt Engineering: Skills to effectively communicate with and direct AI systems for optimal results
- Ethical Considerations: Awareness of bias, privacy concerns, and responsible AI usage frameworks
- AI Integration: Competence in incorporating AI tools into existing workflows and processes
“AI literacy isn’t optional anymore; it’s essential. This includes gaining proficiency in machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. These skills are crucial for understanding how AI tools function, and how they can be effectively applied in cybersecurity,” explains Julian Brownlow Davies, VP of advanced services at Bugcrowd.
The urgency for AI skills development is undeniable, with half of employers planning to re-orient their business in response to AI advancements, two-thirds planning to hire talent with specific AI skills, and 40% anticipating workforce reductions in areas where AI can automate tasks.
Real-World Applications:
- Content Creation: Using generative AI tools to assist with writing, design, and multimedia production
- Decision Support: Leveraging AI analysis to complement human judgment in complex decisions
- Process Automation: Identifying opportunities where AI can streamline workflows and reduce repetitive tasks
- Customer Engagement: Implementing AI-powered solutions to enhance customer interactions while maintaining human oversight
Skill Development Resources:
- Google AI Education – Comprehensive AI learning resources for all levels
- Elements of AI – Free online course on AI fundamentals
- AI For Everyone by Andrew Ng – Beginner-friendly introduction to AI concepts
2. Data Analysis
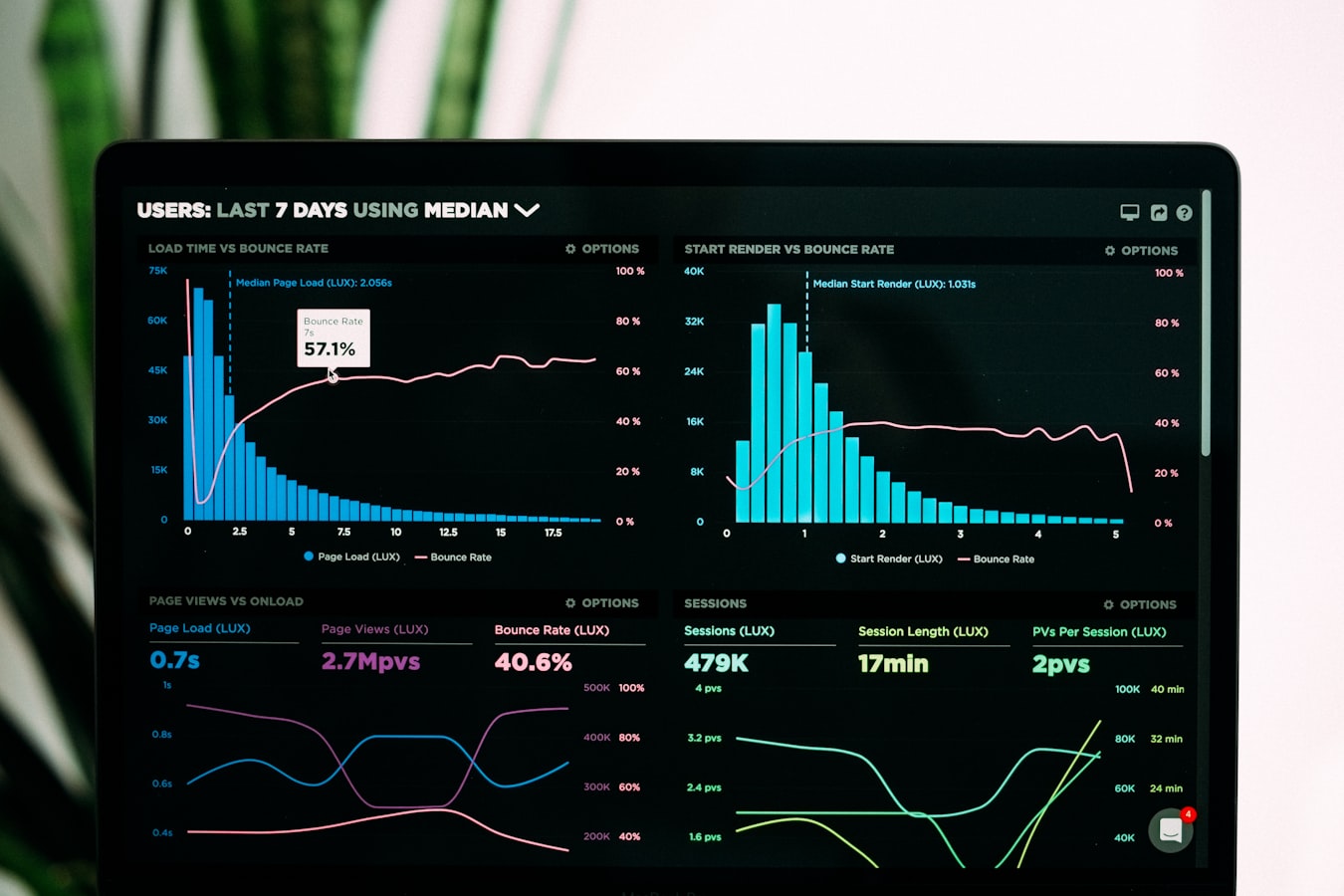
As organizations continue to amass unprecedented volumes of information, data analysis skills have become invaluable across departments. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 ranks “AI and big data” as the top skill expected to grow in importance, with analytical thinking consistently ranking in the top 10 most crucial skills for the future workforce.
Data literacy—the ability to read, work with, analyze, and reason with data—has become a foundational requirement across all business sectors. According to LinkedIn’s Workplace Learning Report, data skills have seen a surge in demand, with companies increasingly building data expertise not just in specialized departments but throughout their organizations.
Core Data Analysis Skills for 2025:
- Advanced Statistical Thinking: Proficiency in probability, correlation, statistical significance, and predictive modeling
- Data Visualization and Storytelling: Creating clear, compelling visual representations that effectively communicate insights to diverse stakeholders
- Critical Data Interpretation: Drawing actionable conclusions from complex datasets while accounting for limitations and biases
- Cross-Platform Tool Proficiency: Mastery of industry-standard data analysis tools and platforms
- Data Ethics and Governance: Understanding principles of responsible data usage, privacy regulations, and bias mitigation
The demand for these skills extends far beyond dedicated analyst roles, with even traditionally non-technical roles now requiring data competencies. Coursera’s Job Skills Report 2025 identified data ethics as among the fastest-growing skills on their platform, driven by the increasing need for employees to responsibly manage and analyze customer data.
| Industry | Increase in Data Analysis Requirements (2023-2025) |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | 68% |
| Retail | 52% |
| Manufacturing | 47% |
| Education | 41% |
| Finance | 39% |
This trend is further amplified by the rise of AI and automation technologies that require human oversight and interpretation of analytics outputs.
Beyond the Spreadsheet:
Modern data analysis involves more than just numbers in cells. Today’s professionals need to:
- Ask strategic questions that align data collection with business objectives
- Implement governance frameworks to ensure data quality and compliance
- Communicate insights across functions using visualization and narrative techniques
- Connect data to actionable decisions that drive measurable business impact
Skill Development Paths:
- Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate – Comprehensive introduction to data analytics
- DataCamp – Interactive learning platform for data skills
- Tableau Training & Tutorials – Resources for data visualization
3. Cybersecurity Awareness

With digital transformation accelerating and remote work becoming permanent, cybersecurity has undergone a fundamental transformation. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, networks and cybersecurity rank as the second fastest-growing skills in importance, closely following AI and big data skills. The report identifies that geoeconomic fragmentation and increasing global tensions are driving a significant surge in demand for these security-related capabilities.
The 2025 job market reflects this reality, with cybersecurity no longer confined to IT departments but recognized as an organization-wide responsibility. Coursera’s Job Skills Report notes a 71% year-over-year rise in cyberattacks, with 93% of organizations experiencing two or more identity-related breaches in the past year, fueling the rapid growth in demand for risk management and cybersecurity skills.
Essential Cybersecurity Knowledge for 2025:
- Advanced Threat Intelligence: Recognizing sophisticated phishing attempts, supply chain vulnerabilities, and emerging AI-driven attack vectors
- Zero-Trust Architecture Understanding: Familiarity with modern security frameworks that verify every access request regardless of source
- Comprehensive Data Protection: Implementing classification schemes for sensitive information with appropriate handling protocols
- Incident Response Planning: Contributing to and understanding organizational response plans for security breaches
- Regulatory Compliance: Awareness of evolving cybersecurity regulations and their implications for daily operations
The financial stakes continue to rise dramatically, with the average data breach in 2024 costing organizations $5.2 million—a figure that doesn’t account for reputational damage and lost customer trust. Organizations increasingly recognize that cybersecurity in 2025 is “less about prevention and is increasingly focused on resilience and soft skills,” requiring adaptability and collaborative approaches to security.
Industry-Specific Security Requirements:
| Industry | Critical Security Skills |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | HIPAA compliance, medical device security, patient data protection |
| Finance | Fraud detection, transaction security, regulatory compliance |
| Manufacturing | OT/IT convergence security, supply chain protection |
| Retail | PCI DSS compliance, e-commerce security, customer data privacy |
| Government | Critical infrastructure protection, classified data handling |
Skill Development Resources:
- Cybersecurity Fundamentals – SANS – Foundational security awareness materials
- HackerOne’s Hacker101 – Free web security courses
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework – Government standards for security implementation
Soft Skills

While technological skills continue to grow in importance, the human elements of work remain irreplaceable. In fact, as automation and AI handle more routine tasks, distinctly human capabilities become even more valuable in 2025’s workplace. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 emphasizes that skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, agility, and curiosity/lifelong learning are among the top skills rising in importance, complementing technological skills.
4. Advanced Communication

Communication skills have always been important, but they’ve evolved dramatically in response to changing work environments, digital transformation, and global collaboration requirements. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 ranks “leadership and social influence” among the top 10 skills on the rise, recognizing the increasingly critical nature of interpersonal and communication capabilities in a technology-saturated workplace.
With hybrid and remote work models becoming permanent fixtures, the demand for sophisticated, multi-channel communication abilities has intensified. LinkedIn’s 2024 Workplace Learning Report ranks communication among the top skills employers seek, noting that “employers are seeking talents with strong interpersonal skills, such as communication, customer service, leadership, and management.”
Advanced Communication Skills in 2025:
- Omnichannel Communication Mastery: Exceptional effectiveness across written, verbal, visual, and digital mediums, with the ability to select the optimal channel for each communication need
- AI-Enhanced Communication: Skill in using AI tools to improve clarity, efficiency, and impact of communications while maintaining authenticity
- Cross-Cultural Digital Fluency: Navigating global and diverse teams with cultural intelligence and awareness of digital communication norms across regions
- Technical-to-Layperson Translation: Ability to explain complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders with clarity and relevance
- Empathetic Digital Communication: Conveying emotional intelligence and human connection through digital mediums where non-verbal cues are limited
According to recent workplace studies, 92% of managers cite communication deficiencies as their primary challenge with underperforming team members, indicating the direct link between communication capability and professional effectiveness.
Communication in the Modern Workplace:
The definition of “good communication” has expanded significantly in recent years. Today’s professionals must master:
- Asynchronous excellence: Conveying complete information without requiring immediate responses
- Multimedia fluency: Incorporating appropriate visuals, audio, and interactive elements
- Digital empathy signals: Using tone and empathy indicators effectively in text-based formats
- Inclusive communication: Ensuring messaging is accessible and appropriate for diverse audiences
Skill Development Approaches:
- Toastmasters International – Public speaking and leadership development
- LinkedIn Learning Communication Courses – Diverse communication skills training
- Crucial Conversations – High-stakes communication methods
5. Adaptability and Resilience

In an era of unprecedented technological and economic disruption, adaptability and resilience have emerged as perhaps the most critical workplace skills. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 ranks “resilience, flexibility and agility” among the top five skills projected to grow significantly in importance through 2030, with creative thinking and curiosity/lifelong learning also within the top five—skills that directly complement adaptive capabilities.
This surge in importance isn’t surprising given the pace of transformation across industries. For 77% of business and HR leaders surveyed, flexibly moving skills between roles is viewed as critical for navigating future disruptions. With approximately 40% of workers’ skills expected to change by 2030, the ability to adapt quickly to new requirements has become a fundamental professional requirement rather than a differentiator.
Components of Modern Adaptability in 2025:
- Strategic Cognitive Flexibility: Systematically reconsidering assumptions and rapidly adopting new frameworks when conditions change
- Uncertainty Management: Not only functioning effectively despite incomplete information but thriving in ambiguous environments by making calculated decisions
- Accelerated Learning Methodology: Employing structured approaches to acquire new knowledge and skills at significantly faster rates than competitors
- Advanced Emotional Regulation: Managing personal stress while helping others navigate organizational transitions effectively
- Change Leadership: Proactively driving necessary transformations rather than merely responding to them
According to the latest workforce research, employees rated highly for adaptability received promotions 2.6 times more frequently than peers with similar technical skills but lower adaptability scores—a statistic that reinforces its growing importance in advancement decisions.
Adaptability in Practice:
- Technology Adoption: Embracing new tools and systems with minimal resistance and maximum exploration
- Role Evolution: Comfortably expanding responsibilities as job requirements change
- Organizational Restructuring: Maintaining productivity and positive engagement during major changes
- Crisis Response: Converting unexpected challenges into innovation opportunities
Developing Adaptability:
- Center for Creative Leadership – Resilience and change leadership programs
- Resilience at Work – Assessment and training tools
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction – Evidence-based resilience building
6. Emotional Intelligence
As automation and AI handle increasingly sophisticated analytical and routine tasks, the uniquely human ability to navigate emotions—both one’s own and others’—has become an essential differentiator in the 2025 workplace. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 highlights that empathy and active listening skills continue to be critical core competencies, particularly as technology advances.
According to LinkedIn’s research, employers are prioritizing candidates with strong interpersonal capabilities alongside technical skills. This reflects a fundamental shift in how organizations view value creation—while machines excel at processing information, humans excel at navigating the complex emotional terrain of organizational life and customer relationships.
Key Emotional Intelligence Components for 2025:
- Advanced Self-Awareness: Sophisticated recognition of one’s own emotional patterns, triggers, and impacts across various workplace contexts
- Emotional Regulation in Digital Environments: Maintaining appropriate emotional responses in both in-person and virtual settings
- Cross-Cultural Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and navigating emotional expressions across diverse cultural contexts
- AI-Human Emotional Interface: Ability to detect when AI interactions require human emotional intervention
- Emotion-Driven Decision Enhancement: Using emotional intelligence to complement data-driven decision processes
Recent research published in workplace psychology journals found that teams led by managers with high emotional intelligence scores outperformed other teams by 28% on key performance metrics. Moreover, emotional intelligence has proven to be particularly valuable during organizational transformations, with high-EQ leaders achieving 31% greater implementation success rates than their lower-EQ counterparts.
Comparative Value Across Roles:
| Role Category | Impact of High EQ | Key Application Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership | Critical | Transformational change, team empowerment, strategic vision |
| Customer-Facing | Very High | Client relationship management, conflict resolution, consultative selling |
| Creative | High | Cross-functional collaboration, feedback integration, audience empathy |
| Technical | Moderate-High | Requirements gathering, stakeholder communication, team integration |
| Administrative | Moderate | Organizational awareness, stakeholder support, priority management |
Skill Development Opportunities:
- TalentSmart EQ Testing & Training – Emotional intelligence assessment and development
- Six Seconds EQ Network – Global emotional intelligence resources
- Center for Nonviolent Communication – Empathy and communication methodology
Digital Collaboration

The continued evolution of remote and hybrid work has cemented digital collaboration as a distinct and critical skill category. Effective professionals in 2025 must navigate virtual environments with the same proficiency as physical workspaces. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, “broadening digital access” is expected to be the most transformative trend overall, with 60% of employers expecting it to transform their business by 2030.
7. Remote Team Effectiveness

Remote and distributed work has evolved from pandemic-driven emergency measures to become a sophisticated, deliberate, and often preferred approach to collaboration. This expanded digital access has accelerated the adoption of remote and hybrid work models. The latest global workforce data indicates that 73% of companies now maintain some form of hybrid or remote work arrangement, with 42% operating fully distributed teams across multiple countries. This shift has created unprecedented demand for professionals who can navigate and lead in virtual environments effectively.
Advanced Remote Team Skills for 2025:
- Digital Psychological Safety Creation: Building environments where team members feel safe to take risks and be vulnerable in virtual settings
- Asynchronous Leadership Excellence: Designing workflows and communication systems that maximize productivity across time zones while respecting work-life boundaries
- Virtual Team Performance Optimization: Using digital tools and behavioral science to enhance distributed team effectiveness
- Remote Visibility and Impact Measurement: Systematically documenting and communicating contributions and outcomes in virtual environments
- Inclusive Virtual Collaboration: Ensuring equitable participation and influence regardless of location, technology access, or working style
The consequences of mastering these skills are significant. Research shows that organizations with highly effective remote work practices report 22% higher productivity, 27% better talent retention, and 41% greater innovation output compared to organizations that merely replicate traditional office practices in digital environments.
Remote Collaboration Maturity Model:
- Basic Remote Capability: Using video conferencing and chat as direct substitutes for in-person interaction
- Intermediate Remote Effectiveness: Implementing structured digital workflows and documentation practices
- Advanced Remote Optimization: Creating systems that maximize asynchronous productivity across time zones
- Remote Excellence: Building culture, innovation, and strategic advantage through intentional distributed approaches
Skill Development Resources:
- Remote.co Resources – Best practices for remote work
- Distributed.com – Tools and training for distributed teams
- GitLab Remote Playbook – Open-source remote work methodology
8. Cross-Cultural Digital Competence

As organizations continue to tap global talent pools and operate across increasingly borderless digital environments, cross-cultural digital competence has emerged as a critical skill for 2025. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 identifies “global citizenship” as an essential skill, particularly as companies navigate geoeconomic fragmentation and expanding digital access across regions.
This capability has taken on new dimensions with the rise of AI translation tools, international remote collaboration, and global talent strategies. The intersection of cultural intelligence and digital communication represents one of the most complex yet valuable skill domains in today’s workplace.
Advanced Cross-Cultural Digital Competencies for 2025:
- Cultural-Digital Context Integration: Sophisticated understanding of how cultural backgrounds influence digital communication preferences, tool adoption, and collaboration patterns
- AI-Mediated Cross-Cultural Communication: Effectively using and compensating for AI translation and communication tools in multicultural settings
- Cultural Power Dynamics Recognition: Identifying and addressing power imbalances that emerge in cross-cultural digital environments
- Global Digital Inclusion Practices: Creating participation structures that accommodate diverse communication styles, technological access levels, and time zones
- Cross-Cultural Digital Conflict Resolution: Developing specialized approaches for addressing misunderstandings and conflicts in international virtual settings
A McKinsey Global Institute study found that companies with the highest levels of national diversity were 35% more likely to outperform their industry median, but only when they actively developed cross-cultural competencies within their teams. Similarly, a 2024 study of global virtual teams found that those with strong cross-cultural digital competence achieved 41% higher project success rates and 37% greater innovation outcomes compared to culturally diverse teams without these specialized skills.
Cultural Dimensions in Digital Collaboration:
| Cultural Dimension | Digital Expression | Adaptation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Power Distance | Meeting structure, decision processes | Clear guidelines on authority and consultation norms |
| Individualism/Collectivism | Credit attribution, decision approach | Balancing individual recognition with team achievements |
| Uncertainty Avoidance | Communication detail, planning horizons | Providing context-appropriate detail and contingency plans |
| Time Orientation | Scheduling expectations, deadline interpretation | Explicit temporal expectations with cultural flexibility |
| Communication Style | Directness, contextual information | Adapting message format for different cultural preferences |
Development Resources:
- Cultural Intelligence Center – Assessment and training for cross-cultural effectiveness
- Hofstede Insights – Cultural dimension tools for global teams
- Global DISC – Cultural communication profiling and development
Continuous Learning
In a rapidly evolving work landscape, the ability to continuously update skills and knowledge has become a non-negotiable professional requirement. Learning agility—the ability to quickly acquire and apply new capabilities—is now recognized as a distinct and valuable skill in its own right. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, “curiosity and lifelong learning” ranks among the top five skills growing in importance.
9. Learning Agility

Learning agility has emerged as a fundamental meta-skill for the 2025 workforce. With nearly 40% of workers’ core skills expected to change by 2030, the ability to learn quickly and effectively has become essential for career sustainability.
Coursera’s Job Skills Report 2025 highlights a critical insight: “The half-life of professional skills continues to shrink,” with technical skills now having an average half-life of just 2-5 years. This accelerated obsolescence cycle demands a sophisticated approach to continuous learning that goes far beyond traditional education or training programs.
Advanced Learning Agility Components for 2025:
- Personalized Meta-Learning Systems: Developing customized approaches to learning based on cognitive preferences, professional context, and specific skill requirements
- AI-Enhanced Knowledge Acquisition: Strategic use of AI tools to accelerate learning processes while maintaining depth of understanding
- Strategic Knowledge Prioritization: Sophisticated evaluation of which skills and knowledge domains will provide highest return on learning investment
- Rapid Experimentation Methodology: Structured approaches to testing and applying new knowledge in low-risk, high-feedback environments
- Dynamic Learning Networks: Building and maintaining relationships with diverse experts who can provide just-in-time knowledge and perspective
According to LinkedIn’s 2024 Workplace Learning Report, learning agility now ranks as the third most important skill for career advancement, behind only leadership and digital literacy. Organizations increasingly view learning agility as a predictor of long-term performance, with 82% of executives rating it as “very important” or “critical” in hiring and promotion decisions.
Learning Agility Framework:
- Identify strategic skill gaps with potential for high career or organizational impact
- Source optimal learning resources personalized to your learning style and needs
- Structure deliberate practice with immediate application opportunities
- Apply knowledge in real contexts as quickly as possible to cement learning
- Reflect and refine both what you’ve learned and how you learn
Development Approaches:
- Degreed – Skill development and tracking platform
- Ultralearning – Accelerated learning methodology
- Learning How to Learn (Coursera) – Science-based learning techniques
AI-Augmented Skills
The relationship between human workers and AI systems has evolved significantly. Today’s professionals need to develop sophisticated skills for effective human-AI collaboration—leveraging AI capabilities while providing uniquely human value. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, half of employers plan to re-orient their business in response to AI developments.
10. AI Collaboration and Augmentation

Beyond basic AI literacy, the most competitive professionals in 2025 are developing sophisticated capabilities for strategic AI integration and collaboration. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 notes that 50% of employers plan to re-orient their business in response to AI, and two-thirds plan to hire talent with specific AI skills—creating unprecedented demand for professionals who can work effectively alongside and enhance AI systems.
This represents a fundamental shift from merely using AI tools to establishing dynamic human-AI collaboration systems that maximize the unique strengths of both. As IBM’s AI literacy initiative explains, “The immediate need is for AI skills, but there will soon be a growing demand for quantum skills, alongside an enduring demand for cybersecurity skills.”
Advanced AI Collaboration and Augmentation Skills for 2025:
- AI-Human Workflow Design: Creating integrated processes that optimize the division of labor between human and AI contributors
- Specialized AI Capability Development: Training and fine-tuning AI systems for domain-specific applications
- AI Output Evaluation and Enhancement: Critically assessing AI-generated content and adding uniquely human dimensions that improve final results
- Ethical AI Implementation Leadership: Guiding organizations in responsible AI deployment that aligns with human values and regulatory requirements
- AI Augmentation Strategy: Developing comprehensive approaches for leveraging AI to enhance human capabilities rather than merely automating existing processes
The competitive advantages of mastering these skills are substantial. Recent research found that professionals who developed specialized AI augmentation skills increased their productivity by an average of 37% compared to those with similar backgrounds using standardized AI approaches. At an organizational level, companies with sophisticated human-AI collaboration systems report 43% greater innovation output and 28% higher customer satisfaction compared to companies that implement AI without rethinking human-AI workflows.
The Human-AI Partnership:
| Task Component | AI Contribution | Human Contribution | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Analysis | Pattern recognition, calculation, prediction | Context understanding, anomaly identification, ethical oversight | Insights that are both data-driven and contextually relevant |
| Content Creation | Draft generation, formatting, fact-checking | Creative direction, emotional resonance, strategic alignment | Material that is technically sound but distinctively compelling |
| Decision Making | Option generation, scenario modeling, historical analysis | Value judgment, stakeholder consideration, ethical reasoning | Decisions that leverage both comprehensive analysis and human wisdom |
| Customer Interaction | Information retrieval, routine response handling | Emotional connection, complex problem resolution, brand embodiment | Service that is both efficient and distinctly human |
Skill Development Resources:
- AI Business School (Microsoft) – AI strategy and implementation resources
- Human-Centered AI Lab (Stanford) – Research and resources on human-AI collaboration
- Partnership on AI – Multi-stakeholder AI implementation guidelines
How to Develop These Skills

Acquiring the top 10 in-demand skills for 2025 requires a strategic approach to professional development. The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 indicates that if the world’s workforce was made up of 100 people, 59 would need training by 2030—a statistic that underscores the scale of the upskilling challenge ahead.
Encouragingly, the report also found that 50% of the global workforce has now completed some form of training as part of their learning and development initiatives—up from 41% in 2023. This trend indicates growing recognition of the importance of continuous skill development across industries.
Formal Education and Certification
While traditional degrees maintain their value, shorter, specialized programs have gained significant credibility with employers responding to the urgent need for specific skill development:
- Microcredentials: Focused certifications in specific skill areas (3-6 months), particularly in high-growth areas like AI, data analysis, and cybersecurity
- Professional Certificates: Industry-recognized qualifications in applied skills that demonstrate practical competence
- Executive Education: Intensive programs for advancing leadership and strategic capabilities in specific contexts
- Specialized Bootcamps: Immersive training experiences focused on rapid skill acquisition in technical domains
According to LinkedIn’s learning research, 85% of employers now plan to prioritize upskilling their workforce, with 70% expecting to hire staff with new skills—creating strong incentives for investment in formal skill development.
Experiential Learning
Practical application continues to be one of the most effective skill development approaches, with increasing emphasis on structured experiential learning:
- Cross-Functional Projects: Volunteering for initiatives that require skills outside your current expertise
- Innovation Labs: Participating in dedicated environments for exploring emerging technologies
- Internal Gigs: Taking on temporary assignments in different departments to build new capabilities
- Simulation Training: Engaging in realistic scenarios that develop skills in low-risk environments
Mentorship and Coaching
Personalized guidance accelerates skill development significantly, with new models emerging to support specialized skill acquisition:
- Reverse Mentoring: Learning from junior colleagues with specialized expertise in emerging technologies
- Skill-Specific Coaching: Working with targeted coaches for high-priority capability development
- Peer Learning Circles: Forming mutual skill development groups with shared learning objectives
- Virtual Communities of Practice: Engaging with global experts in specific skill domains
Continuous Practice
Developing sustainable habits that support ongoing skill building is essential for long-term career success:
- Dedicating 5-10 hours weekly to deliberate skill development with focused practice
- Creating accountability through public commitments and learning partners
- Building reflection practices to consolidate and deepen new knowledge
- Establishing feedback loops to continuously refine capabilities
Industry-Specific Demands

While the top 10 skills have broad applicability, the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 reveals significant industry variations in skill importance and projected growth. Different sectors are experiencing unique transformation patterns driven by their specific technological adoptions, market pressures, and regulatory environments.
Healthcare

The healthcare sector faces a dramatic transformation, with AI and big data projected to see adoption rates exceeding 90% among healthcare employers by 2030. According to the Future of Jobs Report, healthcare increasingly values professionals who combine clinical knowledge with:
- Advanced Health Data Analytics: Sophisticated ability to derive insights from complex patient and population data, incorporating AI-assisted diagnostic capabilities
- Telehealth Excellence: Designing and delivering virtual care experiences that maintain high clinical standards while enhancing accessibility
- Patient Experience Architecture: Creating integrated healing journeys across physical and digital touchpoints that optimize both outcomes and satisfaction
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Facilitating effective coordination across medical specialties, support functions, and technology teams in increasingly complex care environments
- Healthcare AI Governance: Ensuring responsible implementation of AI in clinical settings with appropriate human oversight
Technology

According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, the technology sector is experiencing the most dramatic skill transformation, with advancements in AI and information processing expected to transform 86% of businesses by 2030. The report shows that beyond core technical expertise, technology companies in 2025 specifically seek professionals skilled in:
- Ethical AI and Technology Implementation: Ensuring responsible innovation through structured frameworks that address bias, privacy, transparency, and societal impact
- Human-Centered Technology Design: Creating solutions that meaningfully address human needs while acknowledging cognitive and social realities
- Complex Technology Storytelling: Translating technical capabilities into accessible narratives that connect with business stakeholders and end users
- Agile Technology Leadership: Guiding cross-functional teams through rapid iteration cycles while maintaining strategic alignment
- Technology Sustainability Integration: Implementing practices that reduce the environmental impact of technology development and deployment
Financial Services

According to the World Economic Forum’s research, financial services are experiencing a significant transformation driven by both technological change and economic volatility. The industry particularly values:
- Advanced Regulatory Technology Competence: Leveraging AI and data analytics to navigate increasingly complex compliance requirements across multiple jurisdictions
- Financial Technology Ecosystem Integration: Orchestrating traditional financial services with fintech innovations, blockchain applications, and embedded finance solutions
- Sophisticated Risk Intelligence: Developing comprehensive approaches to identifying, quantifying, and mitigating emerging financial, operational, and systemic threats
- Financial Wellness Advisory: Guiding clients through increasingly complex financial landscapes with a focus on holistic wellbeing outcomes
- AI-Enhanced Financial Analysis: Combining AI capabilities with human judgment to derive superior investment and risk management insights
Manufacturing
The Future of Jobs Report 2025 indicates that manufacturing is experiencing profound transformation through robotics, automation, and sustainability imperatives. Modern manufacturing professionals need advanced skills in:
- Resilient Supply Chain Architecture: Designing adaptable, multi-sourced systems that can withstand regional disruptions and geopolitical tensions
- Digital Twin Orchestration: Creating, maintaining, and deriving strategic insights from comprehensive virtual representations of physical production systems
- Circular Manufacturing Implementation: Developing production approaches that eliminate waste through materials innovation, product design, and end-of-life reclamation
- Advanced Human-Robot Collaboration: Optimizing the division of labor between humans and increasingly capable robotic systems while ensuring worker safety and satisfaction
- Smart Factory Systems Integration: Connecting IoT sensors, edge computing, and analytics platforms to create intelligent manufacturing environments
Education

The World Economic Forum’s research reveals that educational institutions are facing dual pressures to adopt new technologies while maintaining human connection. They increasingly seek professionals skilled in:
- Immersive Learning Experience Design: Creating pedagogically sound experiences that seamlessly blend physical, digital, and extended reality environments
- AI-Enhanced Educational Personalization: Leveraging artificial intelligence to provide individualized learning pathways while maintaining instructor guidance and peer interaction
- Competency-Based Assessment Systems: Developing sophisticated approaches to evaluating real-world skills and capabilities beyond traditional testing methods
- Digital Wellbeing Integration: Incorporating strategies that promote healthy technology usage, digital citizenship, and psychological safety in learning environments
- Workforce-Aligned Curriculum Development: Creating educational content that anticipates evolving skill demands based on workforce trend analysis
Future Outlook

Looking beyond 2025, the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report identifies several emerging trends that will likely shape skill demands in the coming years. These trends represent both significant opportunities and challenges for professionals seeking to future-proof their careers.
The Rise of Environmental Expertise
The Future of Jobs Report 2025 identifies environmental stewardship among the top 10 fastest-growing skills, reflecting the increasing business importance of sustainability. As climate challenges intensify, organizations are rapidly developing specialized environmental capabilities:
- Advanced Carbon Accounting and Management: Sophisticated approaches to measuring, reporting, and actively reducing organizational climate impact across complex value chains
- Circular Economy Transformation: Redesigning entire business models and operations to eliminate waste and regenerate natural systems
- Climate Risk Integration: Incorporating climate vulnerability assessments into strategic planning, infrastructure development, and investment decisions
- Sustainability Leadership: Effectively leading organizational transformation toward environmental goals while balancing stakeholder interests
- Environmental Technology Implementation: Deploying and managing emerging technologies specifically designed to address environmental challenges
Quantum Computing Integration
While still emerging, quantum computing is beginning to influence skill requirements more significantly. The World Economic Forum notes that as quantum capabilities mature, organizations will need professionals who understand:
- Industry-Specific Quantum Applications: Identifying and implementing quantum computing solutions for domain-specific challenges in areas like material science, logistics, and financial modeling
- Quantum-Classical Systems Architecture: Designing hybrid computing environments that leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical approaches
- Quantum Security Implementation: Developing and deploying post-quantum cryptography protocols to protect against emerging computational threats
- Quantum Algorithm Design: Creating algorithmic approaches tailored to quantum computing’s unique capabilities and limitations
Extended Reality Ecosystem Development
The convergence of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality technologies is creating demand for professionals who can navigate and create within these emerging digital environments:
- Spatial Computing Strategy: Developing comprehensive approaches to leveraging three-dimensional digital environments for business, educational, and entertainment purposes
- Cross-Reality Experience Architecture: Designing seamless user journeys that move between physical and multiple virtual contexts while maintaining coherence
- Immersive Collaboration Systems: Creating effective team environments that function across physical and virtual presence
- Extended Reality Ethics and Governance: Establishing frameworks for responsible development and use of immersive technologies
- Physical-Digital Integration: Connecting virtual experiences with real-world objects, locations, and activities through IoT sensors and advanced interfaces
Frequently Asked Questions

How quickly are in-demand skills changing?
According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025, approximately 40% of workers’ core skills are expected to change by 2030. The half-life of professional skills—the time it takes for half of learned knowledge to become obsolete—continues to shrink dramatically. Technical skills now have an average half-life of just 2-5 years, though this varies significantly by field. The report indicates that technological skills are projected to grow in importance more rapidly than any other type of skills, with AI and big data, networks and cybersecurity, and technological literacy leading this growth.
Which skills offer the best return on investment?
The World Economic Forum’s research suggests that skills that are both widely applicable and difficult to automate typically provide the strongest career benefits. The combination of technological literacy (particularly in AI) and advanced human capabilities (like creative thinking, resilience, and leadership) consistently shows the highest correlation with career advancement and compensation growth. The report specifically identifies skills that differentiate growing from declining jobs as: resilience/flexibility/agility, resource management, quality control, and programming/technological literacy—suggesting these offer particularly strong returns.
How can organizations support skill development?
The Future of Jobs Report 2025 indicates that forward-thinking organizations are implementing multiple approaches to workforce development in response to the 63% of employers who cite skills gaps as the biggest barrier to business transformation:
- Comprehensive upskilling strategies, with 85% of surveyed employers planning to prioritize workforce development
- Targeted hiring for new skills, with 70% of employers expecting to recruit staff with emerging capabilities
- Structured transition pathways, enabling 19% of workers to be upskilled and redeployed within their organizations
- AI-enhanced learning technologies that deliver personalized development at scale
- Strategic workforce planning that anticipates future skill needs rather than reacting to current gaps
How do skill requirements differ globally?
The World Economic Forum’s regional analysis shows that while core skills remain valuable worldwide, their relative importance and specific applications vary significantly by region:
- Asia-Pacific: Higher emphasis on AI/big data skills and technological literacy, with Eastern Asia particularly focused on addressing aging population challenges
- Europe: Greater prioritization of sustainability skills and regulatory navigation capabilities in response to ambitious climate policies
- Middle East and North Africa: Increasing focus on adaptability and cost management skills in response to economic pressures
- North America: Strong emphasis on AI adoption and cybersecurity capabilities due to rapid technological transformation
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Growing demand for digital literacy skills as digital access expands, creating new economic opportunities
Conclusion

The skills landscape of 2025 reflects profound transformations in how we work, collaborate, and create value. The World Economic Forum’s comprehensive research with over 1,000 companies representing 14 million workers reveals that while technological capabilities continue to grow in importance, they increasingly need to be paired with distinctly human strengths like creative thinking, resilience, and ethical judgment.
As technological advancements, demographic shifts, geoeconomic tensions and economic pressures reshape global labor markets, creating 170 million new jobs while displacing 92 million others by 2030, the imperative for proactive skill development has never been greater.
The most successful professionals recognize that skill development is no longer a periodic activity but a continuous process embedded throughout their careers. By proactively building the top 10 in-demand skills identified in this article—and developing the meta-skill of learning agility—they position themselves not just for current opportunities but for long-term career resilience in an increasingly dynamic professional landscape.
What skills are you focusing on developing this year? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below!
Research Methodology: This article synthesizes findings from multiple authoritative sources, including the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2025 (based on data from over 1,000 companies representing more than 14 million workers across 22 industry clusters and 55 economies), LinkedIn’s Workplace Learning Report, Coursera’s Job Skills Report 2025, and interviews with industry experts across sectors. The skill rankings consider projected growth importance, differentiation between growing and declining roles, and cross-industry applicability.
Editor’s Note: This article is updated quarterly to reflect the latest research and market trends. Last reviewed April 2025.























